Introduction
As an efficient new type of crushing equipment, Mineral sizer plays a significant role in the crushing operations of open-pit and underground mines both at home and abroad. The structural design rationality of its core working component - the crushing roller teeth - directly determines the service life of the equipment, the power consumption of crushing, the production capacity and the quality of the output particle size. Therefore, in the design and application process of Mineral sizer, the shape selection and design method of the crushing roller teeth have become key technical challenges. This article conducts an in-depth analysis of the actual operation status of Mineral sizer, systematically sorts out the main reasons for the damage of the crushing roller teeth, and proposes targeted improvement measures, aiming to provide theoretical basis and practical guidance for equipment optimization and maintenance.
Analysis of Wear Causes
Material impact caused the peeling of the wear - resistant coating
During the mining production process, when large pieces of crushed materials in the stripping are conveyed by the Heavy Duty Apron Feeder and fall towards the Twin Shaft Mineral sizer, due to the large drop, the large pieces of materials exert a strong impact on the surface of the crushing roller teeth. This kind of impact force can easily cause the wear-resistant coating on the surface of the roller teeth to fall off locally, exposing the base metal to a harsh abrasive environment and significantly accelerating the wear.
The welding performance of the substrate is poor
The welding performance of the base material of the crushing roller teeth directly affects the bonding quality of the wear-resistant coating. If the substrate is improperly selected or its welding process performance is poor, it will lead to insufficient bonding strength between the coating and the substrate. During use, the coating is prone to peeling off, thereby significantly reducing the service life of the mineral sizer roller teeth.
Improper selection of welding rods
During the surfacing repair process of wear-resistant coatings, if the chemical composition, hardness and toughness of the selected electrodes do not match, not only will an effective wear-resistant protective layer not be formed, but cracks may also be caused by welding stress concentration, accelerating the failure and wear process of the coating.
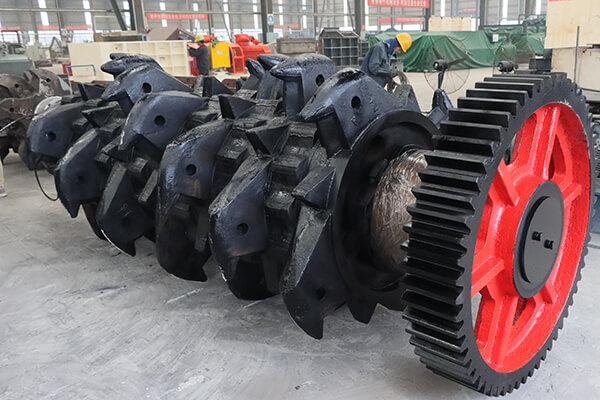

Analysis of the Causes of Fracture
The tooth profile design is unreasonable
If the tooth profile structure of the crushing roller teeth is not properly designed, it will lead to uneven stress distribution during operation and local stress concentration. When mineral sizers encounter large pieces of material or difficult-to-break material, the roller teeth are subjected to high-intensity impact loads and are highly prone to breakage in stress concentration areas.
Manufacturing defects lead to poor installation fit
During the casting and machining processes, if the teeth of the crushing roller have internal defects such as shrinkage cavities and slag inclusions, or if the processing accuracy of the mating surface between the tooth shape and the tooth seat is insufficient, it will result in the inability of the roller teeth and the tooth seat to achieve an ideal fit. This poor fit will cause uneven load distribution and significantly increase the risk of roller tooth breakage.
Materials adhere to the joint surface
In actual operation, fine-grained materials tend to adhere to the joint surface between the teeth of the crushing roller and the tooth seat, causing changes in the installation gap and deterioration of the force state. Under long-term operation, this interference phenomenon will cause additional bending moments and impacts, eventually leading to fatigue fracture of the roller teeth of mineral sizer.
Improvement measures
Improvements for coating peeling and wear
Control the feeding height and buffer design
By optimizing the relative layout between the feeder and the mineral sizer, the material drop is reduced. Or, buffer baffles, wear-resistant liners and other devices can be added at the feeding port to reduce the direct impact of large pieces of material on the roller teeth.
Select the preferred base material and surfacing welding process
Alloy steel with good welding performance is adopted as the base material for the roller teeth, and hard alloy welding wire with high hardness and high toughness is selected for surfacing welding. By standardizing the welding process parameters, the metallurgical bond between the wear-resistant coating and the base is ensured, and the impact resistance and anti-spalling ability of the coating are improved.
Promote the integral casting of wear-resistant roller teeth
For extremely harsh working conditions, mineral sizer can choose integrally cast crushing roller teeth made of wear-resistant steel. These roller teeth have the advantages of uniform structure, high strength and good wear resistance, but the casting process must be strictly controlled to avoid casting defects.
Improvements to roller teeth breakage and joint surface problems
Optimal design of tooth profile structure
Based on modern design methods such as finite element analysis, the tooth profile of the crushing roller teeth is simulated and optimized to ensure uniform stress distribution and avoid stress concentration. The overall load-bearing capacity and impact resistance of the roller teeth can be enhanced by increasing the fillet radius at the tooth root and optimizing the tooth profile curve.
Improve manufacturing and assembly accuracy
Strictly control the processing quality of the crushing roller teeth and tooth seats to ensure that the dimensional and positional tolerances of the mating surfaces meet the design requirements. Optimize the assembly process to ensure that the roller teeth and tooth seats of mineral sizer fit tightly and avoid abnormal force caused by poor fit.
Strengthen quality inspection and operation and maintenance
Comprehensive non-destructive testing (such as ultrasonic and magnetic particle testing) should be carried out on the teeth of the crushing rollers before they leave the factory to promptly identify and eliminate products with internal defects. During daily operation, the adhering materials on the mating surface between the roller teeth and the tooth seat should be regularly cleaned to keep the contact surface clean and ensure that the force state meets the design expectations.
Conclusion
The damage to the teeth of Mineral sizer crushing rollers mainly results from two types of problems: wear and breakage. The causes involve multiple links such as design, materials, manufacturing, process and operation management. Take targeted improvement measures, optimize the tooth profile design, select high-performance materials, improve the manufacturing process, standardize the use and maintenance, and enhance the service life of the crushing roller teeth and the reliability of the mineral sizer operation.