The Apron feeder is a continuous feeder for bulk materials (such as coal and ores). Due to its huge supply capacity and long installation distance, it can withstand the direct impact of large quantities of materials and maintain stable performance. Therefore, it has been widely used in industries such as ports and mining. However, in actual project engineering, the uncertainty in usage often leads to spillage caused by chain plate sticking.
Heavy Duty Apron feeder
The Heavy Duty Apron Feeder is widely used in the mining, metallurgy, construction materials, and coal industries. This machine is mainly used for continuously and short-distance conveying various large-sized materials under the specific pressure of the silo and the funnel below. It is not only used for processing coarse particles but also for fine materials. It is suitable for crushing, screening, and transportation equipment, especially for initial crushing. The heavy work can be completed in harsh environments. It is highly adaptable to the particle size composition, temperature, viscosity, and material changes (such as frost, rain, snow, or ice) of the materials. The supply is uniform, accurate, and reliable. The machine can be installed horizontally or diagonally, and the maximum upward transportation angle is 23 degrees.
Working principle of Apron feeder
The Heavy Duty Apron feeder uses the power of an electric motor to drive the sprocket shaft. This sprocket shaft rotates through a coupling and a reducer. The sprocket engages with the chain pin and pulls the chain plate for continuous straight motion. The chain plate is supported by the supporting wheels and the supporting wheels attached to the frame, and the tensioning device is adjusted to ensure that the chain meshes correctly with the sprocket, thus achieving the purpose of material transfer. The Heavy Duty Apron feeder mainly consists of the drive unit, chain plate unit, tensioning unit, frame, supporting wheels and chain support wheels, and main shaft unit.
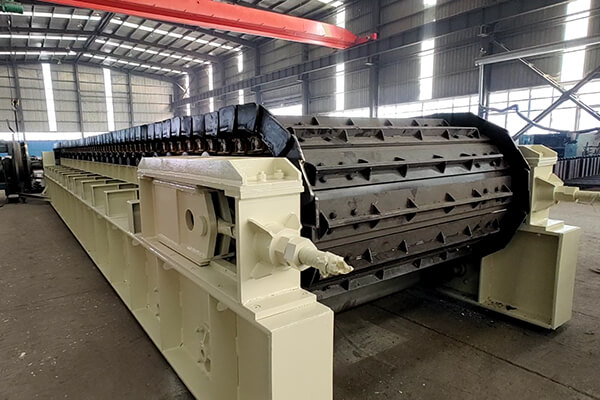

Characteristics of the Apron Feeder Structure Drive device
The drive unit is the power core of the apron feeder, usually consisting of an electric motor, coupling, reducer, sprocket shaft and sprocket. The power output by the electric motor is transmitted to the reducer through the coupling, and then drives the sprocket to rotate, which in turn drives the chain and the chain plate to perform continuous linear motion, thereby achieving uniform material transportation. Some models are also equipped with torque rods and locking discs to improve the transmission stability. Depending on the working conditions, they can be driven by electric, hydraulic or pneumatic methods.
Tightening device
It is a screw tightening mechanism, mainly composed of two supporting rollers. The ends of the two supporting rollers are composed of rolling bearings, bearing seats, composite springs and tightening screws. The supporting rollers are fixed on the shaft through expansion sleeves. At each end of the shaft, there are two rows of radial spherical roller bearings and bearing seats, which are installed on the sides of the frame and slide back and forth between the guide rails. The tightening device is used to adjust the horizontal position of the chain, and the supporting rollers serve as the guide and support for the chain plate to ensure appropriate chain tension and smooth movement.
Chain plate device
The chain plate device consists of slot plates, chain links and other parts. The slot plates are of single arc joint type and are welded with low alloy steel plates, which are of high strength, wear-resistant and leak-free. For the chain link type, a bulldozer track chain (tank chain) manufactured by a specialized manufacturer was selected. The chain link of this track chain has small pitch error, smooth movement, high strength, large tension and no lubrication. Rack
This is a I-beam structure formed by welding steel plates. Many rib plates are welded between the upper and lower convex flange plates. The two I-shaped main beams are composed of many channel steel sections. The I-beam structure is fully welded throughout and is very sturdy and stable.
Supporting wheels
The supporting wheels consist of components such as bearings, rolling bearings, shafts, rollers, sealing rings, and covers. They are mainly used to support the operating parts of the chain and prevent the chain plate from generating significant interference due to load and self-weight. When the chain operates normally, it can withstand the influence of certain materials and the pressure of the silo, and even limit the deviation of the chain.
Supporting chain wheels
The supporting chain wheels consist of components such as bearings, rolling bearings, shafts, rollers, sealing rings, and covers. They mainly support the empty chain plate and prevent the weight of the chain plate from causing a heavy empty chain plate and affecting normal operation.
Main shaft device
The main shaft device is composed of shafts, bearing boxes, chain wheels, support wheels, bearing seats, etc. Two chain wheels installed on the shaft drive the chain plate to move continuously, achieving the purpose of transportation and supply. The characteristic of this device is that the chain wheels and support wheels are connected by expansion sleeves, and the main shaft is mounted on the output shaft of the reducer. Its simple disassembly and maintenance are very convenient.
Reasons for the adhesive material on the apron feeder chain plate
After the apron feeder has been in use for some time, the chain plate becomes sticky. Since the chain plate often bears the impact of the ore, it is usually equipped with transverse reinforcing ribs to strengthen the chain plate. When relatively damp powder-like materials adhere to the bottom of the reinforcing ribs and the chain plate moves from the loaded part to the return part, sometimes the deposits will fall and eventually accumulate on the ground, which not only pollutes the environment but also does not help the safe operation of the apron feeder. Solid deposits only appear on the top of the apron feeder (with a length of within 1m), and basically have no tail section. The deposits are cleaned approximately every half a month, which brings some workload to the maintenance personnel. The analysis of the equipment causes are as follows.
The actual moisture content of the feed does not match the information provided in the technical contract. If the water content is too high, the material will become wet and sticky, making it easier to adhere to the apron feeder. Due to the large amount of falling objects during the dump truck operation, spray dust suppressants are installed at the top and bottom outlets of the hopper to prevent a large amount of dust and protect the working environment. When the conveyor system is running, the spray dust control device will spray a large amount of water mist, which will increase the surface moisture of the material and increase the possibility of material adsorption. Setting transverse reinforcing ribs on the chain plate makes the surface of the chain plate protrude, which affects the smoothness of the surface and increases the possibility of material adsorption. For sticky materials, it is usually necessary to install cleaning equipment at the bottom of the apron feeder to collect the fallen materials. However, the Apron feeder used in this project does not have a cleaning device, so it is impossible to achieve automatic collection of sticky materials.
Solution
The head of the apron feeder is equipped with a roller brush cleaner. On each side of the apron feeder at the bottom of the funnel, a square hole is made to pass the roller brush cleaner through, and then it is fixed to the head funnel along the direction of the roller. The roller brush cleaner has an automatic drive unit and can be used in conjunction with the feeder. When the apron feeder is running, the roller brush will also rotate in the opposite direction to perform cleaning. The equipment modification work for this scheme is very small, the modification cycle is short, and the reconstruction cost is very low. The cleaning effect of the roller brush is very good, but due to the soft touch and poor wear resistance of the plate brush, the reliability is relatively poor.
Improve the smoothness of the bearing surface of the chain plate. The adhesion points of the apron feeder are mainly located at the root of the transverse reinforcement ribs of the chain plate. Therefore, if an attempt is made to make a smooth transition between the reinforcement ribs and the surface of the chain plate, the adhesion of the material may decrease. Therefore, a 10mm thick steel plate is made into a 36mm wide bar, with its length the same as the length of the chain plate reinforcement. The bar is set at 30 degrees, and many repair works are carried out by welding the inclined angle weld to the reinforcement ribs to fill the angle between the reinforcement ribs and the surface of the chain plate. However, during the modification, the chain plate does not need to be removed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when using the Heavy Duty Apron feeder to transport viscous materials, the following measures can be taken to avoid the viscous substances in the materials: use special-shaped reinforcing ribs on the chain plates to smooth the surface of the chain plates. If the material's descent is small and has little impact on the chain plates, the reinforcing ribs can be removed. This can save the initial investment of the project and be more effective. A cleaning chain has been added at the bottom of the Apron feeder. This method has significantly increased the initial investment of the project, but it can achieve reliable and leak-free feeding. It is hoped that the above methods will achieve good results and can serve as a reference for similar problems of heavy-duty Apron feeders.





.jpg)






