Introduction
Banana Screen is applied in multiple industries such as mining, sand and gravel aggregates, coal, and metallurgy. It can quickly achieve material classification, impurity removal and dehydration. The performance of the sieve plate directly determines the screening effect, operational stability and comprehensive usage cost of the equipment. The aperture accuracy and opening rate of the sieve plate will directly affect the screening accuracy and processing capacity.
Selection of materials for Banana Screen sieve plates
Characteristics of screening materials
Material properties are the primary factors in determining the selection of screen plate materials, among which hardness, wear resistance and particle size have the most significant influences. For materials with high hardness (Mohs hardness above 6) and strong wear resistance, such as granite and basalt, if materials with insufficient wear resistance are selected, the screen plate will suffer severe wear in a short period of time, resulting in an increase in pore size and a decrease in screening accuracy. For materials with low hardness and low wear resistance such as coal and limestone, there is no need to overly pursue highly wear-resistant materials.
Instead, common materials with better cost performance can be chosen. At the same time, the size of the material particles also needs to be given special attention - when screening fine particle materials, the aperture of the sieve plate is relatively small, and the anti-clogging performance of the material needs to be considered; When screening coarse-grained materials, the impact of the materials on the screen plate is greater, so materials with strong impact resistance should be given priority.
Operating conditions of the equipment
The operating parameters and usage environment of Banana Screen will directly affect the service life of the screen plate. From the perspective of equipment parameters, for the Banana Screen with a high vibration frequency and large amplitude, the alternating impact force on the screen plate is stronger. At this time, materials with good toughness and excellent fatigue resistance should be selected to avoid cracking of the screen plate due to long-term vibration. In production lines with large processing volumes, the material pressure per unit area of the screen plate is greater, and the strength requirements for the material are also higher.
From the perspective of the usage environment, in scenarios that are humid, dusty or contain corrosive media (such as sand and gravel yards by the sea, slurry screening in mineral processing plants), corrosion-resistant materials should be given priority to prevent the screen plates from rusting or being corroded and damaged. In high-temperature environments (such as the screening of hot materials in the metallurgical industry), materials that can withstand high temperatures and are not prone to aging should be selected.
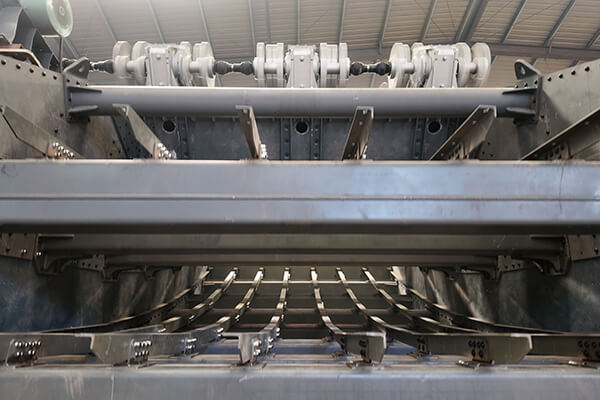

Screening accuracy requirements
The requirements for screening accuracy vary greatly among different industries, which also affects the selection of screen plate materials. For instance, in the precision mineral processing or chemical industry, it is necessary to screen out materials with uniform particle size distribution, and the consistency and stability of the sieve plate aperture are extremely high. At this time, materials with high processing accuracy and not easy to deform (such as stainless steel) should be selected.
In industries such as construction sand and gravel where precision requirements are relatively loose, materials with low processing difficulty and lower cost (such as carbon steel) can be selected. In addition, the surface smoothness of the sieve plate material also affects the screening accuracy - if the surface is too rough, it is easy for fine particle materials to adhere, causing the sieve holes to be blocked and affecting the screening effect.
Common sieve plate materials for Banana Screen
Carbon steel screen plate
Carbon steel screen plates are mainly made of low-carbon steel through stamping or cutting processes to form screen holes. They have moderate hardness and excellent processing performance. They can be made into screen plates with different hole diameters and opening rates according to requirements, and the raw materials are widely available. The advantage lies in its low cost. Whether it is raw material procurement or processing and manufacturing, the cost is much lower than that of high manganese steel, stainless steel and other materials, making it suitable for users with limited budgets.
However, it has poor wear resistance. When screening materials with high hardness and high wear resistance, the screen surface is prone to wear, causing the pore size to expand. Moreover, it has poor corrosion resistance and is prone to rust in damp or corrosive media environments. It is suitable for screening materials with low hardness and low wear resistance, such as coal, limestone (Mohs hardness 3-4), coal gangue, etc. It is not recommended for screening highly wear-resistant ores in mines or for long-term use in damp environments.
High manganese steel screen plate
High manganese steel Screen plates are usually made of high manganese steel materials such as ZGMn13. They have excellent impact resistance and can withstand the severe impact of coarse particle materials without deforming or breaking easily. They are very suitable for the high-frequency vibration working characteristics of Banana screens. The structural strength of high manganese steel screen plates is high, making them suitable for production scenarios with large processing volumes and less likely to deform due to material accumulation.
Polyurethane screen plate
Polyurethane screen plates are made of polyurethane elastomers as raw materials and formed through injection molding or casting processes. They feature high wear resistance and diverse screen hole designs, allowing for various combinations of hole diameters such as square, circular, and rectangular. It has a long service life. When screening materials with high wear resistance, its service life can reach 2 to 3 times that of high manganese steel and 5 to 8 times that of carbon steel.
The light weight can effectively reduce the load of the Banana Screen body and decrease the energy consumption of the equipment operation. The self-lubricating property and elasticity of the polyurethane surface can effectively prevent the adhesion of sticky materials, and it has a high screening efficiency, especially suitable for the screening of materials with high moisture content.
Tips for extending the service life of Banana Screen sieve plates
Select materials based on the actual working conditions
When used in cold regions, polyurethane screen plates should be avoided. Instead, high manganese steel or ceramic composite screen plates can be used. When screening viscous materials, if metal screen plates are selected, anti-sticking coatings should be added to the screen surface or screen plates with special opening designs should be chosen.
Regular inspection and maintenance
Regularly inspect the condition of the screen plate once, clean the residual materials on the screen surface to prevent local wear or deformation of the screen plate due to material accumulation. Check whether the connecting bolts between the screen plate and the screen frame are loose. If they are loose, tighten them in time to prevent the screen plate from shifting or colliding during vibration. When local wear or cracking of the sieve plate is found, repair or replace the local components in time to prevent the damage from expanding.
Control the screening parameters reasonably
When screening coarse-grained materials, appropriately reduce the vibration frequency and increase the amplitude to minimize the impact force of the materials on the screen plate. When screening fine particle materials, increasing the vibration frequency and reducing the amplitude can enhance the screening efficiency while preventing material blockage. Control the feeding volume to be uniform and stable to avoid excessive instantaneous feeding causing the screen plate to operate under overload. A buffer device (such as a buffer plate) can be set at the feeding port to reduce the direct impact of materials on the screen surface.
Conclusion
The selection of the Screen plate material for Banana Screen needs to be based on a comprehensive understanding of the working conditions. It is necessary to clarify the key characteristics such as the hardness, wear resistance, particle size and moisture content of the screened materials. Combined with the operating parameters of the equipment, vibration frequency, processing capacity, usage environment, temperature, humidity and corrosiveness, materials with suitable performance should be screened out.





.jpg)






