Introduction
Tubular drag conveyors can convey various materials ranging from fine powder and granules to fragile granules, and are widely used in multiple industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, mining and agriculture. Unlike traditional open conveying systems, chain tube conveyor operates in a closed pipe, minimizing material loss and preventing contamination.
The core of Tubular drag conveyors is a volumetric conveying system, which uses chains or cables equipped with discs to convey materials smoothly and efficiently through sealed pipes. This article will delve into the working principle, key components, types and advantages of tubular drag conveyors, as well as their comparison with other common conveying technologies.
The working principle of Tubular drag conveyors
Working principle
Tubular drag conveyors operate based on the principle of volumetric conveying. They achieve material conveying by replacing a fixed volume of materials in a closed channel. The space between the continuous discs in the pipe forms discrete closed material volumes. As the chain moves, these material volumes are pushed forward.
Operation mode
Starting from the feed port, bulk materials are sent into the sealed pipeline. After the materials enter, they will fill the space between two adjacent discs attached to the continuous chain. Driven by a motor to provide mechanical force, the chain assembly moves within the pipe. The disc is designed to closely adhere to the inner wall of the pipe with an extremely small gap, functioning as a pusher to smoothly push the trapped material forward. When the assembly reaches the discharge port, the material is released, and the empty disc continues to return to the feed port, usually through a return pipe or a loop structure of the same pipe.
The advantages of low-speed transportation
One notable feature of Tubular drag conveyors is their low operating speed. Unlike high-speed conveying systems, which may cause material damage through impact, friction or centrifugal force, the slow and smooth movement of discs can minimize shear stress and wear to the greatest extent. Low-speed operation not only maintains the integrity of the materials, but also reduces noise, lowers energy consumption, and extends the service life of conveyor components such as discs, chains/cables, and pipes.
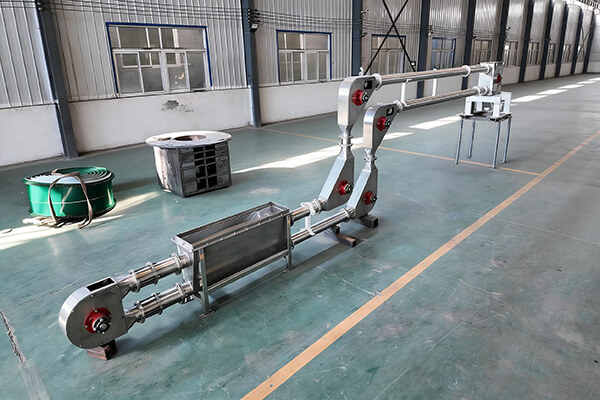

A key component of Chain tube conveyor
Conveying pipeline
The choice of pipe material depends on the application requirements, among which stainless steel and carbon steel are the most commonly used options. Stainless steel is preferred for food, pharmaceutical and chemical applications due to its corrosion resistance, easy cleaning property and compliance with FDA and EHEDG standards. On the other hand, carbon steel is an economical choice for heavy industrial applications such as mining and construction, where corrosion is not a major issue.
Chain
Chains or cables are the driving elements that pull the disc through the pipe. The choice between the two depends on the application requirements. The chain is suitable for heavy-duty applications, capable of withstanding higher load capacity and operating in high-temperature environments. They also have stronger wear resistance and are suitable for conveying abrasive materials such as sand and gravel.
Disk
The disc is a component that directly contacts and moves materials. Common materials include nylon, which is cost-effective and has good impact resistance. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has excellent chemical resistance and is suitable for corrosive materials. And ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), which is highly wear-resistant, has a low coefficient of friction, and meets the FDA food application standards.
Driven tensioning
The drive is usually composed of a motor, a reducer and a drive sprocket for the chain. The motor speed is adjustable, enabling precise control of the conveying speed. The tensioning device is usually located at the other end of the drive station and is crucial for maintaining the optimal tension of the chain or cable.
Feeding port and discharging port
The tubular drag conveyor has a high degree of flexibility in material feeding and discharging, and can support multiple feeding ports and discharging ports. Multiple feed ports allow materials to be fed into the conveyor from different sources (such as multiple hoppers), which is very useful for mixing or combining different materials. Multiple discharge ports enable the conveyor to distribute materials to different destinations (such as storage silos, processing equipment) without the need for additional conveyors.
A comparison between tubular drag conveyors and other conveying technologies
Comparison with screw conveyors
The screw conveyor uses rotating screw blades to scrape materials through the trough. It has significant limitations in handling abrasive materials and long-distance transportation. Abrasive materials such as sand and gravel can cause rapid wear of the screw blades and the trough, increasing maintenance costs. Screw conveyors are inefficient in long-distance transportation. In contrast, tubular drag conveyors use closed pipes and low-friction discs, minimizing wear caused by abrasive materials. They are also more efficient in long-distance transportation, capable of transporting materials up to 1000 feet or more, with no significant power loss.
Comparison with scraper conveyors
Scraper conveyors rely on chains to drive scrapers to convey materials within the trough. They are often used in harsh working conditions such as heavy loads and high temperatures. However, they have problems such as excessive material residue, high maintenance difficulty, and easy shear damage to the materials. The hard contact between the scraper and the tank body not only causes significant wear and increases maintenance costs, but also may lead to the residue of fine powder materials due to the scraper gap, making it difficult to clean.
It is not suitable for industries with strict hygiene requirements such as food and pharmaceuticals. Tubular drag conveyors adopt a sealed pipe and flexible disc push design, avoiding hard friction between materials and conveying components. This can not only reduce material damage but also lower equipment wear. At the same time, the sealed structure can prevent material residue and contamination, and the cleaning difficulty is much lower than that of the scraper conveyor.
Comparison with pneumatic systems
The pneumatic conveying system uses air pressure to transport materials through pipelines. It requires large compressors to generate the necessary air pressure, which incurs high energy costs and is prone to material stratification problems. By contrast, chain tube conveyor has lower energy consumption due to its low-speed operation and low-friction design. Its volumetric conveying principle can also prevent material stratification, as each material volume moves as an independent unit.
Conclusion
Tubular drag conveyors is a multifunctional, efficient and reliable solution suitable for bulk material conveying in multiple industries. Its sealed pipe design, low-speed operation and flexible layout make it an ideal choice for applications that require clean, gentle and efficient transportation. It can meet the needs of handling heavy, abrasive materials and fragile food-grade products.
When choosing chain tube conveyor, material properties, load capacity, hygiene requirements and installation space should be considered to make a choice between chain and cable systems.


.jpg)









