Introduction
In the screening processes of industries such as coal, mining, and metallurgy, the screening accuracy directly affects the quality of the final products and the production efficiency. Among various screening equipment, the wobbler feeder is highly favored for its excellent screening accuracy and stable operation performance. So, what makes the roller screen achieve high precision screening? The secret does not lie in a single factor, but in the perfect combination of its ingenious structural design and intelligent operation concept - from the plum blossom-shaped sieve rollers that can achieve self-cleaning and prevent blockages, to the uniform sieve gap that determines the classification basis;from the inclination and rotational speed that can balance processing capacity and efficiency, to the independent drive technology that endows it with powerful shearing and sorting capabilities; at the same time, its excellent adaptability to material properties and meticulous protective design jointly form the efficient, precise and reliable screening foundation of the roller screen. This article will deeply analyze and reveal the technical core behind the high precision screening of the roller screen, and help you understand the technical essence behind it.
Factors Affecting Screening
Structure and Parameters
Shape and Structure of the Screen Roll
Circular Screen Roll: The most commonly used, simple to manufacture, but prone to blocking materials that are close to the sieve gap size.
Heart-shaped Screen Roll: The screen surface of the Roller Screen is wavy. During rotation, it can produce throwing and stirring effects on the materials, having a self-cleaning function, which can effectively reduce blockages and improve screening efficiency.
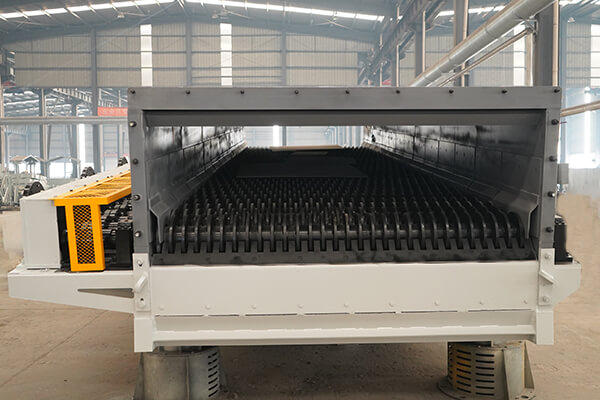

Sieve Gap Size
Absolute Factor: The sieve gap size directly determines the maximum particle size of the material that can be screened out theoretically. This is the basis for screening accuracy.
Uniformity: The gaps between all screen rolls must be consistent; otherwise, the screening accuracy of the Roller Screen will decrease, and some qualified materials will not be screened out.
Screen Surface Inclination Angle
Large Inclination Angle: The material flow speed is fast, and the processing capacity is high, but the material stays on the screen surface for a short time, resulting in insufficient screening and lower efficiency. The processing capacity will decrease, and the material may accumulate easily.
Small Inclination Angle: The material flow speed is slow, the stay time is long, the screening is more thorough, and the efficiency is high. However, the processing capacity will decrease, and the screen holes are prone to clogging, especially for wet materials.
Usually Set: The Roller Screen usually has a fixed inclination angle (such as 12°-15°) to balance the processing capacity and efficiency.
Screen Roll Rotational Speed
High Rotational Speed: The stirring effect of the screen roll on the material is strong, which is conducive to screening and can prevent wet and sticky materials from adhering. However, it will shorten the material stay time, and some materials may not be able to be screened out before being carried away.
Low Rotational Speed: The material stays for a long time, but the stirring and self-cleaning effect on the material is weak, which can easily cause clogging of the screen holes, especially for wet materials.
Driving Method
Central Drive: All screen rolls are driven by a large motor through chains or gears. The structure is simple, but the power consumption is high, and the speed of individual screen roll cannot be adjusted. The flexibility is poor.
Individual Drive: Each screen roll or each group of screen rolls is driven by an independent motor and reducer. The advantages are huge: adjacent screen rolls can operate at different speeds, forming stronger shearing and combing effects, which greatly prevent blockages and adhesion. It is convenient for maintenance, and the failure of a single screen roll does not affect the operation of the wobbler feeder. It is easy to achieve variable frequency speed regulation.
Material Characteristics
Particle Size Composition of Materials
"Difficult-to-Screen Particles" Content: The content of particles with a size close to the sieve gap size (usually defined as 0.7-1.5 times the sieve gap size). The more such particles there are, the more likely they are to get stuck in the sieve gap, resulting in a sharp decline in screening efficiency and a reduction in the effective diameter of the sieve holes.
Fine Powder Content: An appropriate amount of fine powder helps the materials to be loose, but too much fine powder (especially when combined with moisture) will stick to the coarse particles or form clumps, hindering screening.
Material Humidity
Water will increase the viscosity of fine particles, causing the materials to stick together and adhere to the screen roll surface, resulting in severe clogging and blockage, and the screening efficiency will almost drop to zero when the moisture content of the materials exceeds a certain critical value (usually 8%-12%, depending on the materials).
Particle Shape of Materials
Spherical or cubic particles are easy to screen through.
Flaky, needle-like, or elongated particles are prone to causing blockages.
Material Density and Fluidity
Materials with high density and good fluidity (such as dry sand) are easy to screen and convey forward.
Materials with low density and loose structure (such as damp clay) are prone to accumulation and adhesion.
The performance of Roller Screen
Sieve face inclination angle
To facilitate the discharge of materials on the sieve, the sieve face of Roller Screen is generally installed at an incline. The size of the inclination angle is related to productivity and screening efficiency. A larger inclination angle means that the materials move forward on the sieve face at a faster speed, resulting in higher production capacity, but the time that materials stay on the sieve face is shortened, reducing the chance of particles passing through the sieve, and thus affecting the screening efficiency.
Sieve face width and length
The wider the sieve face, the greater the processing capacity. However, it is affected by the structure of the Roller Screen sieve frame and other factors, and generally does not exceed 2.5. The width of the sieve face affects productivity, and the length of the sieve face affects screening efficiency. A longer sieve face means that materials stay on the sieve face for a longer time, have more opportunities to pass through the sieve, and thus has a higher screening efficiency. In fact, the width of the sieve face also has an impact on screening efficiency, and the length of the sieve face has an impact on screening capacity.
Sieve plate shape
The sieve holes come in various shapes. The choice of which sieve plate mainly depends on the particle size of the screened materials and the requirements for the use of the screened products. Rectangular sieve holes are easy to allow strip-shaped or sheet-shaped particles to pass through.
Operation and Maintenance of Roller Screen
(1) The Roller Screen is installed on the system and can achieve interlocking operation with the system. When starting, the Roller Screen should be started first, followed by the conveyor belt machine; when stopping, the conveyor belt machine should be stopped first, then the Roller Screen, to ensure smooth interlocking operation.
(2) It is strictly prohibited to start the Roller Screen under load. Before each shutdown, it is necessary to ensure that there is no material on the screen surface before performing the shutdown operation.
(3) After the Roller Screen is put into operation, it is necessary to regularly observe its movement status and replace the lubricating oil regularly. The replacement cycle should be determined according to the actual operating conditions and corresponding operation procedures should be formulated.
(4) When replacing the screen plate, first remove the baffles on both sides of the screen box, then remove the fixing bolts of the bearing seat, then remove the elastic pin coupling, and finally remove the screen shaft. Only then can the screen plate be replaced.
(5) The Roller Screen uses an integrated reducer and motor reducer motor. The motor protection adopts an overheat relay protection device.
(6) When the screen shaft is blocked by iron pieces, wood chips, etc., the pin on the coupling will automatically break, causing the screen shaft to stop rotating, ensuring the safety of the equipment.
The operation status of the Roller Screen
(1) The Roller Screen is driven by a single-axis system. Each set of sieve shafts is equipped with a drive unit, and if any one of the sieve shafts fails, the coal can be pushed by the previous sieve shaft and continue to move forward. The coal sieve can still operate normally.
(2) There is a bypass in the sieve. When necessary, the raw coal can bypass the screening and directly fall into the lower coal collecting bin. An electric baffle is set at the entrance of the Roller Screen. The baffle is made of ZGMn13 material, with a single plate thickness of 12mm. The baffle can be linked with the main coal conveying control system and can automatically switch.
(3) Under normal operation conditions, the screening efficiency of the Roller Screen is 60% to 80%.
(4) This equipment has nylon pin shafts. They serve as an overload protection device to ensure the safety and reliability of the equipment.
(5) The Roller Screen is equipped with a cleaning device. Through this cleaning device, the coal and debris on the gear shaft can be effectively removed.
(6) Both ends of the sieve shafts have good sealing to prevent dust from leaking out.
(7) The frame is made of a box-type structure welded with steel plates to ensure that the frame has sufficient strength.
(8) To facilitate maintenance, an inspection door should be set on the outer shell of the Wobbler Feeder. The joint surface of the inspection door should be tightly sealed, and there should be no phenomenon of dust spilling out or air leakage during the operation of the equipment.


.jpg)









