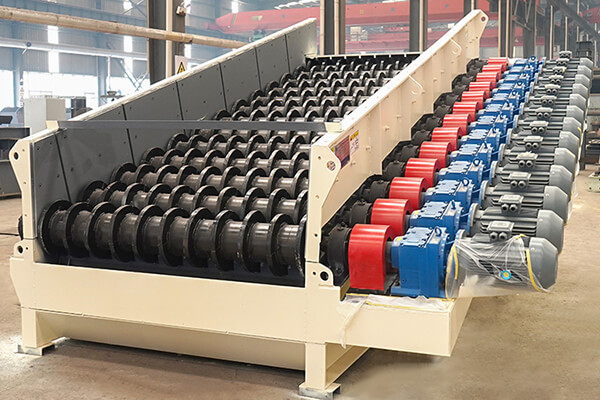
I. About the Roller Screen
The roller screen is a highly efficient screening device. Its screening area is formed by the main shaft bearing of each drum rotating in the same direction, achieving material separation and transportation. Also known as a swing feeder or disc screen, the roller screen is suitable for a wide range of materials and can handle wet and sticky substances. Compared with traditional vibrating screens, the roller screen is less prone to clogging, thereby ensuring processing capacity and screening efficiency. Thanks to its outstanding advantages, our roller screens are widely used in the mining industry.
The working principle of the roller screen involves multiple parallel drum shafts in the screening area, with several staggered screening discs mounted on the shafts. As the drum shafts rotate in the same direction, they realize both feeding and screening of materials.
The core components of a roller screen include the screen box, drive unit, shaft assembly, and cleaning system. The shaft assembly comprises the motor, reducer, shaft, screening discs, parallel keys, locknuts, couplings, bearing seats, and their accessories. The drive motor connects to the reducer and screening shaft via a coupling.

II. Pre-Start Preparations
1. Equipment Inspection
Mechanical Components: Check whether the roller shafts rotate smoothly and whether any screening discs are loose or worn. If the disc edge thickness is worn by more than 1/3, it should be replaced. Ensure bolts on the bearing seats and drive units are tight and the chain tension is appropriate.
Electrical System: Test the motor direction to ensure that all rollers rotate in the same direction or as designed. Check that the control panel instruments, sensors, and blockage switches function properly, and that the emergency stop button is responsive and reliable.
Material and Environment: Clean the screen surface and feed inlet of the roller screen, ensuring no foreign objects such as metal blocks or wood pieces are stuck. Confirm that materials in the feed bin meet equipment requirements.
2. Parameter Settings
Adjust the spacing between rollers based on particle size requirements. For example, when screening coal, the spacing can be set to 50–100 mm; when screening ore, the spacing can be 100–200 mm. For models with variable frequency drives, set the motor speed to 70% of the rated speed at startup, then adjust to the optimal speed after stable operation.
3. Personal Protection
Operators of the roller screen must wear proper protective gear such as safety helmets, dust masks, and gloves.
III. Operation Procedures
Roller screen operation consists of four main steps: startup, feeding, screening process control, and shutdown. Below are detailed instructions.
1. Startup
Power on and check instruments and indicator lights. Start the motor and transmission system according to the operating procedures. Let the machine run unloaded for 2–5 minutes to observe normal operation.
2. Feeding
Feed materials evenly and continuously, maintaining an appropriate accumulation of material. Avoid feeding large foreign objects that could cause clogging.
3. Screening Process Control
Observe the screening performance at the output end. Adjust the shaft rotation speed as needed. If supported by the equipment, adjust the spacing between screening shafts for different materials.
4. Shutdown
Stop feeding and allow the roller screen to run until all materials are discharged. Then turn off the motor, cut the power, and clean the equipment.
IV. Maintenance and Care
Cleaning Tasks: Use a high-pressure blower or broom to remove material adhering to the screening discs and rollers, especially between disc gaps to prevent clogging and ensure efficiency. For wet materials, rinse the screen surface with clean water, then dry or air-dry it. Be especially cautious to protect the motor from water exposure.
Component Inspection: Monitor the temperature of the roller bearings. If overheating occurs, check lubrication or for bearing wear. Inspect the chain for wear; if chain elongation exceeds 2%, tighten or replace it. Replace belts showing cracks.
Lubrication and Maintenance: Lubricate bearings and gearboxes regularly—typically after every 200 hours of operation. Replace lubricant every six months.
V. Safety Precautions
While the roller screen is operating, personnel must stay away from rotating shafts to ensure safety. It is strictly forbidden to open protective covers or reach into the roller area. Wear required PPE such as helmets and protective gloves.
Before maintenance, always disconnect power and hang a "Do Not Energize" warning sign. Electrical maintenance must be performed by qualified electricians.
When cleaning or adjusting the upper rollers, use stable scaffolding or a lift platform to prevent falls. Avoid foreign objects like metal blocks or large rocks that could damage the shafts. If screening efficiency drops, inspect the roller spacing or check for entangled material. Regularly monitor bearing temperatures to avoid overheating.
If abnormal conditions such as smoke or strong vibration occur, immediately press the emergency stop button and report to the on-duty personnel before troubleshooting.
Our roller screens are of premium quality and supported by comprehensive services provided by experienced engineers and specialized tools, all aimed at maximizing your profitability.





.jpg)






