Apron feeders and belt feeders play a crucial role in bulk material handling in modern industry.
Although they both serve in material transportation, there are significant differences in design structure, performance, application scenarios and other aspects. An in-depth understanding of these differences can help companies make accurate selections, improve production efficiency and reduce operating costs.
What is an apron feeder
Apron Feeders, also known as apron Conveyors, consist of a series of overlapping steel plates or disks that are mounted on a chain equipped with rollers. The thickness of the steel plates is usually between 10 - 50mm, customized to suit the application, and this heavy-duty construction gives it a high load carrying capacity.
Materials
The apron feeder is designed to handle heavy, abrasive materials such as boulders and ores, and can even cope with highly viscous materials that tend to stick to the surface of the equipment. It has an excellent conveying capacity of up to 5,000 tons per hour and can handle lumps up to 2,000 mm in size. It easily conveys raw ore in mines and waste materials in waste incineration plants.
Advantages
The advantages of this equipment are its ability to handle heavy materials stably, the overlapping design of the steel plates effectively prevents materials from overflowing or clogging, and the heavy-duty construction gives it excellent abrasion and impact resistance, which allows it to operate stably under harsh working conditions.
What is a belt feeder
A belt feeder, also known as a belt conveyor, has a rubber belt as its core component and is driven by a series of pulleys.
The belt is flat in shape, and common materials include rubber, PVC, nylon and so on. Different material belts are suitable for different working conditions, for example, rubber belts have good abrasion resistance and are suitable for conveying most regular materials; PVC belts are widely used in food, chemical and other industries with high hygiene requirements.
Applicable materials
Belt feeder is good at handling light to medium weight bulk materials, such as sand, gravel, coal, grain, etc. The size of materials that can be handled generally does not exceed 150mm, and the conveying capacity can reach up to 1000 tons per hour.
In the grain processing industry, it can stably convey grains; in the coal conveying system of power plants, it can also efficiently complete the task of coal conveying.
Advantages
The advantages are lower initial cost, relatively simple equipment design, more convenient installation, maintenance and repair, which can save time and resources. At the same time, the flexibility of the rubber belt allows it to flexibly adapt to changes in material flow, reducing the risk of material overflow or clogging.
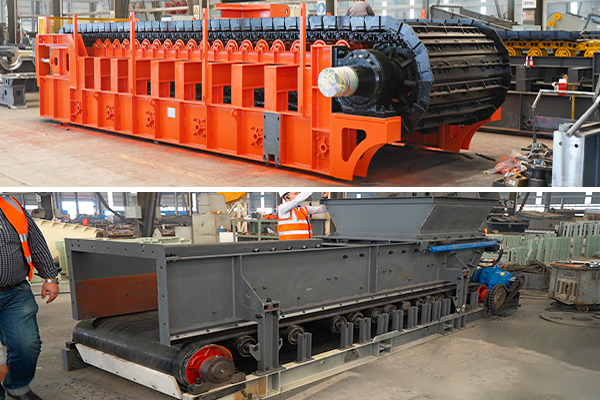

Apron Feeder vs Belt Feeder
In the material conveying process of modern industrial production, choosing the right feeding equipment is of vital importance. Apron feeders and belt feeders, as two common conveying devices, have distinct characteristics in design and performance.
A thorough understanding of their differences can help enterprises make more scientific and reasonable equipment selection decisions based on their specific production needs.
From the perspective of core components in design and construction, belt feeders use flexible rubber belts as the material conveying medium and are driven by pulley systems. This design makes the overall structure of belt feeders relatively simple.
The soft rubber belt can flexibly adapt to different conveying paths and layout requirements. On the other hand, apron feeders use sturdy steel plates or discs as conveying units and are driven by chain roller systems. The unique steel plate or disc structure, combined with chain roller transmission, endows apron feeders with strong load-bearing capacity and wear resistance.
However, in terms of structural complexity, apron feeders are significantly more complex, especially in the assembly of chains and steel plates, which not only involves numerous components but also has relatively high technical requirements for installation and maintenance.
In terms of performance parameters, there are also significant differences between the two.
Load capacity
Belt feeders excel in handling light to medium-weight bulk materials, such as grains and fertilizers, which are small in particle size and light in weight. These materials do not exert excessive pressure or wear on the rubber belt, allowing the belt feeder to complete the conveying task efficiently and stably.
Apron feeders, on the other hand, are experts in conveying coarse, heavy, and large-sized materials, such as ores, coal, and large castings. Their sturdy steel plates and powerful chain roller drive systems enable them to handle these heavy and large-volume materials with ease, ensuring stable operation under heavy loads.
Operating speed
One of the major advantages of belt feeders is their high operating speed, which can reach up to 3m/s or even higher. This high-speed operation characteristic allows for rapid and continuous material conveying, greatly improving the efficiency of material transportation. It is particularly suitable for production scenarios with high requirements for conveying efficiency and large material handling volumes. In contrast, the operating speed of apron feeders is relatively slow, typically ranging from 0.05 to 0.5m/s. Although the speed is not an advantage, it focuses more on the stability and controllability of the material conveying process. For applications that require high stability in the conveying process and precise control of material flow, such as quantitative feeding of ores and slow movement of large castings, apron feeders can excel due to their low-speed stable operation.
Wear resistance
Belt feeders demonstrate high conveying efficiency when dealing with soft and fine materials. However, when encountering sharp and abrasive materials or operating in high-temperature environments, the rubber belt is prone to wear and tear, significantly affecting its service life. In contrast, the steel plates and chain components of apron feeders have excellent wear resistance and can handle such challenging materials with ease. Even when conveying materials like quartz sand and iron ore, which are hard and highly abrasive for long periods, the key components of apron feeders can maintain good performance, making the equipment more durable and reliable than belt feeders.
Maintenance and Cost Comparison
Maintenance Requirements
Belt feeders require daily attention to belt tension, alignment, and cleanliness, and regular inspections of pulleys, rollers, and belt surfaces to prevent material spillage or belt deflection; apron feeder require regular lubrication and inspection of the chain and rollers, although their robust construction reduces the frequency of failures of critical components.
Cost difference
from the initial purchase cost, the belt feeder has obvious advantages; but in the long-term use process, the belt feeder due to belt wear and other issues, the maintenance cost is relatively high; apron feeder although the initial investment is large, but because of its durability, the later maintenance costs are relatively low.
Comparison of environmental adaptability
Belt feeder can operate stably in a clean and dry environment. Once it is in a humid, dusty or chemical erosion environment, its performance will be greatly affected if it lacks a perfect sealing and cleaning system. The apron feeder, with its robust structure and material, can still maintain stable performance in dusty, humid and even high-temperature environments.
Applicable Scene Analysis
Belt Feeder Applicable Scene
light industry
widely used in food processing industry, such as flour, grain conveying; chemical raw material conveying, such as fertilizer, plastic granule transportation; building materials production of cement, gypsum powder conveying and other scenes.
Heavy industry (small and medium-sized materials)
it plays an important role in the conveyance of ore fines in mineral processing plants, coal conveyance system in power plants, and small and medium-sized aggregate conveyance in sand and gravel quarries, etc. It is suitable for production scenarios that are more sensitive to the conveyance efficiency and cost.
Applicable scenes of apron feeder
Mining and metallurgical industry
it is an indispensable equipment in the conveying of raw minerals in open pit mines, and the conveying of sinter and coke in iron and steel mills, etc. It is capable of coping with the conveying of heavy loads, large lumps, and high-impact materials.
Building materials and heavy industry
commonly used in the feeding of large materials before crusher, such as granite, concrete block conveying; in the waste incineration plant waste conveying, also become the first choice by virtue of its excellent durability and reliability.
What feeder type is best for your scalping screen?
Material characteristics first
Give full consideration to the weight, size, abrasiveness, viscosity and other characteristics of the material. If the material is light, small and medium-sized particles, the belt feeder can meet the demand; if it involves heavy, large, abrasive materials, the apron feeder should be preferred.
Output demand matching
According to the required conveying capacity and speed, reasonably match the performance of the equipment. For the pursuit of high conveying efficiency of enterprises, the belt feeder high-speed operation of the obvious advantages; for the need for stable, uniform conveying material scene, the apron feeder low-speed controllable characteristics are more appropriate.
Adaptation to the use of the environment
According to the actual use of environmental conditions, such as humidity, temperature, dust and other conditions to choose a strong adaptability of the equipment. In harsh environments, apron feeder can ensure stable operation; in regular clean environments, belt feeders can realize efficient conveying at a lower cost.
Cost Budget Tradeoffs
Comprehensively evaluate the initial investment, maintenance costs, and long-term operating costs. For companies with limited budgets, belt feeders are preferred, while for companies with sufficient budgets and high durability requirements, apron feeder are more cost-effective in the long run, despite their high initial cost.
Conclusion
With flexible conveying, low cost and high efficiency, belt feeders perform well in lightweight, small and medium-sized particulate materials and regular production scenarios; while apron feeder, with the advantages of rigid loading, high wear resistance and resistance to heavy loads, have become a good choice for heavy materials and harsh working conditions.
Enterprises in the actual selection process, the need for a comprehensive synthesis of material characteristics, production requirements, the use of the environment and cost budget and other factors, accurate selection of the appropriate feeder, so as to achieve efficient production and maximize economic benefits.